中国科学院南海海洋研究所边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室施祺研究员团队联合生态环境部华南环境研究所、南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)等单位,在南海珊瑚礁区碳收支研究取得重要进展,首次定量计算了南海珊瑚礁区碳收支。
海洋中的珊瑚礁区汇聚了大量碳酸盐,是重要的碳酸盐库,同时,钙化作用会产生CO2,使得珊瑚礁区表现为大气CO2的源。查明珊瑚礁区二氧化碳的收支总量,对于应对碳达峰-碳中和具有重要意义。南海珊瑚礁分布广泛,从南部的曾母暗沙到北部的台湾恒春半岛均有分布,其总面积约8000 k㎡。近年来,研究团队对南海不同纬度、不同地貌类型的珊瑚礁区海气CO2交换通量、有机碳储量及碳酸钙储量进行了统计分析。
研究结果显示,南海珊瑚礁每年向大气释放约0.37‒1.59×105吨碳,是大气CO2的源,而每年进入珊瑚礁区沉积物的碳储存量高达1.66‒3.78×106吨碳(>98%为碳酸盐沉积),这一数值远超海‒气界面的二氧化碳排放量。南海珊瑚礁在碳储存方面具有重要作用,是海洋碳汇的重要组成。

南海珊瑚礁图片
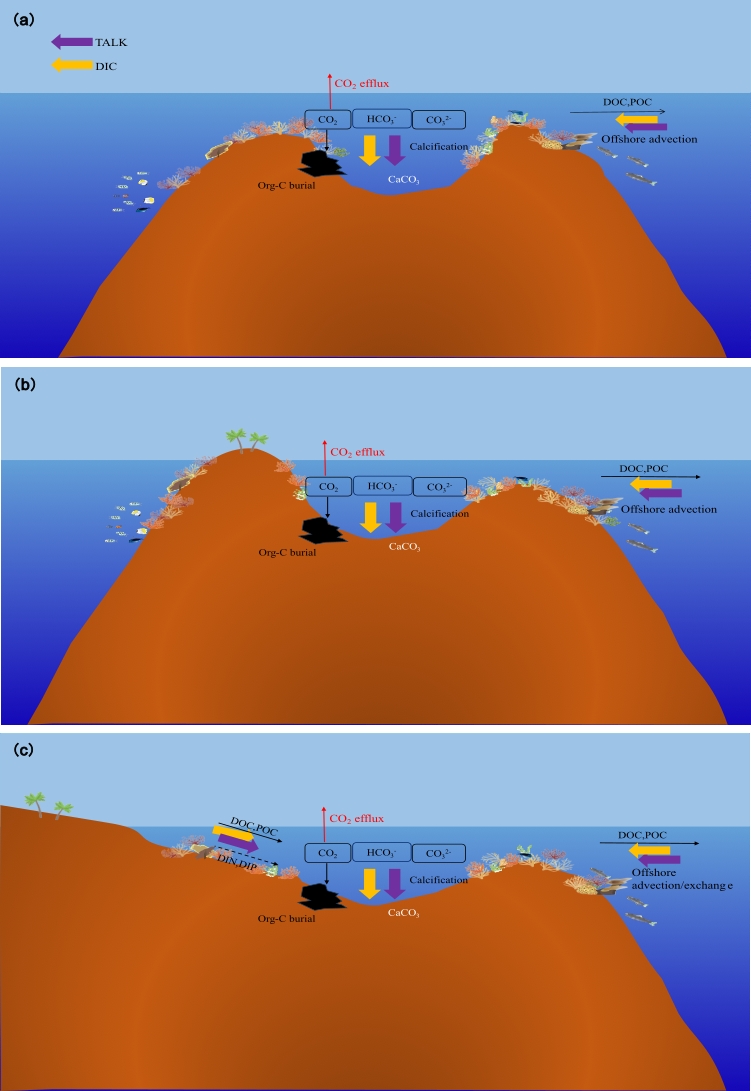
不同地貌类型珊瑚礁区碳循环过程示意图
上述研究成果发表在Frontiers in Marine Science和Regional Studies in Marine Science等上。中国科学院南海海洋所副研究员严宏强为论文的第一作者,博士陶士臣和研究员施祺为论文共同通讯作者。
上述研究工作得到国家自然科学基金、国家重点研发计划以及广东省自然科学基金等支持。
相关论文信息:
Yan,H.,Shi,Q.,Xu,L.,Zhang,H.,Zhao,M.,Tao,S. Carbon budgets of coral reef ecosystems in the South China Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science,2024,11:1335662. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1335662
Yan,H.,Tao,S.,Xu,L.,Shi,Q.,Wang,Y.,Zhao,M.,Zhou,S.,Liu,X. Distribution and air-sea fluxes of CO2 in coral reefs in the Greater Bay Area,China. Regional Studies in Marine Science,2024,80: 103895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2024.103895
Yan,H.,Shi,Q.,Yu,K.,Tao,S.,Yang,H.,Liu,Y.,Zhang,H.,Zhao,M. Regional coral growth responses to seawater warming in the South China Sea. Science of The Total Environment,2019,670: 595-605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.135
Yan,H.,Yu,K.,Shi,Q.,Lin,Z.,Zhao,M.,Tao,S.,Liu,G.,Zhang,H. Air-sea CO2 fluxes and spatial distribution of seawater pCO2 in Yongle Atoll,northern-central South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research,2018,165: 71-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2018.06.008
Yan,H.,Yu,K.,Shi,Q.,Tan,Y.,Liu,G.,Zhao,M.,Li,S.,Chen,T.,Wang,Y. Seasonal variations of seawater pCO2 and sea-air CO2 fluxes in a fringing coral reef,northern South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research- Oceans,2016,121(1):998-1008. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JC011484
Yan,H.,Yu,K.,Shi,Q.,Tan,Y.,Zhang,H.,Zhao,M.,Li,S.,Chen,T,Huang,L.,Wang,P. Coral reef ecosystems in the South China Sea as a source of atmospheric CO2 in summer. Chinese Science Bulletin,2011,56(7):676-684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4372-8
附件下载:


